Disposal Policies
Disposal Policies
Disposal Schedule
Disposal schedules set the minimum requirements for the maintenance, retention or destruction actions to be taken in the existing or future intellectual entities in this repository. A intellectual entity may only be destroyed as part of a disposal process governed by the disposal schedule assigned to that entity. It is the intellectual entity’s disposal schedule that determines how long a record is retained and how it is subsequently disposed of at the end of its retention period.
1. What is a disposal schedule?
MoReq2010® states “Disposal schedules are critical to managing records because MoReq2010® specifies that a record in an MCRS may only be destroyed as part of a disposal process governed by the disposal schedule assigned to that record. It is the record’s disposal schedule that determines how long a record is retained and how it is subsequently disposed of at the end of its retention period.”
RODA supports three types of disposal actions:
- Retain permanently;
- Review at the end of the retention period;
- Destroy at the end of the retention period.
The retention period calculation uses the retention trigger element identifier and add its value with retention period. The possible values for retention period are:
- No retention period;
- Days;
- Weeks;
- Months;
- Years.
2. What categorizes a disposal schedule?
The following attributes categorizes a disposal schedule:
| Field | Description | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
| Title | The identifying name or title of the disposal schedule | True |
| Description | Description of the disposal schedule | False |
| Mandate | Textual reference to a legal or other instrument that provides the authority for a disposal schedule | False |
| Scope Notes | Guidance to authorised users indicating how best to apply a particular entity and stating any organisational policies or constraints on its use | False |
| Disposal Action | Code describing the action to be taken on disposal of the record (Possible values: Retain permanently, Review, Destroy) | True |
| Retention trigger element identifier | The descriptive metadata field used to calculate the retention period | True (If Disposal action code is different from Retain permanently) |
| Retention period | Number of days, weeks, months or years specified for retaining a record after the retention period is triggered | True (If Disposal action code is different from Retain permanently) |
3. Record life cycle
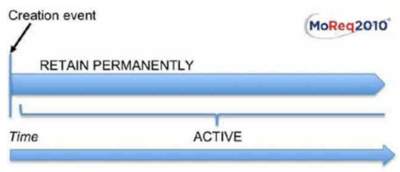
Permanent retention life cycle
This type of disposal schedule, with no retention trigger, has the effect of preventing the calculation of a retention start date and a subsequent retention period.
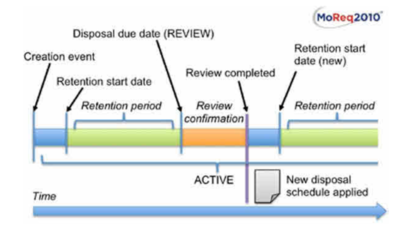
Review life cycle
When a record’s disposal action is set to review, it is not immediately subject to destruction. Instead, the outcome of the review must include the application of a disposal schedule to the record based on the review decision. The new disposal schedule will replace the previous disposal schedule associated with the record and will then specify the ultimate fate of the record, or it may be used to schedule another later review, or to retain the record permanently.
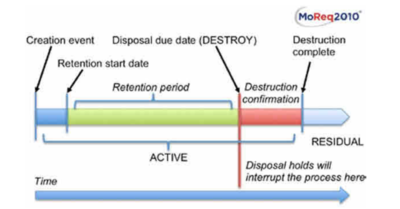
Destruction life cycle
The destruction of records is subject to particular constraints. How records are destroyed will depend on the nature of the content of their components. RODA allows to prune descriptive metadata using XSLT (eXtensible Stylesheet Language Transformations). All the files associated to the record are destroyed leaving the record in a destroyed state.
Disposal Rules
1. What is a disposal rule?
Disposal rules are a set of requirements that determine the disposal schedule for each intellectual entity in this repository. The disposal rules can be applied at any time in order to maintain the repository consistency. Disposal rules can also be applied during the ingest process. Disposal rules have a priority property in which they are executed. If a record is not covered by any of the rules, it will not be associated to a disposal schedule.
2. What categorizes a disposal rule?
The following attributes categorizes a disposal rule:
| Field | Description | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
| Order | Priority order which the rules will be applied in the ingest process or apply process | True |
| Title | The identifying name or title of the disposal rule | True |
| Description | Description of the disposal rule | False |
| Schedule | Disposal schedule that will be associated to a record | True |
| Selection method | Condition that will trigger the disposal rule (Possible values: Child of, metadata field) | True |
3. Selection method
Selection method is the mechanism responsible for matching the rules with the records in the repository and applying the disposal schedule.
There are two types of selection method available on RODA:
- Child of: if the record is directly under a certain AIP.
- Metadata field: if the record has a descriptive metadata value.
4. How it works?
Disposal rules can be applied during ingest process via a plugin or if desired can be applied to the repository at any moment. AIP with disposal schedules associated manually have the option to be override or kept as it is.
Disposal Holds
1. What is a disposal hold?
Disposal holds are legal or other administrative orders that interrupts the normal disposal process and prevents the destruction of an intellectual entity while the disposal hold is in place. Where the disposal hold is associated with an individual record, it prevents the destruction of that record while the disposal hold remains active. Once the disposal hold is lifted, the record disposal process continues.
2. What categorizes a disposal hold?
The following attributes categorizes a disposal hold:
| Field | Description | Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
| Title | The identifying name or title of the disposal hold | True |
| Description | Description of the disposal hold | False |
| Mandate | Textual reference to a legal or other instrument that provides the authority for a disposal hold | False |
| Scope Notes | Guidance to authorised users indicating how best to apply a particular entity and stating any organisational policies or constraints on its use | False |
3. How it works?
When a disposal hold is associated to a record this will prevent the record from being destroyed via disposal workflow and blocks the record of being deleted as well. To gain control over the record the disposal hold needs to be disassociated or lifted.